What is MAC address?
Every computer or device on the Internet has two types of addresses: the first is the physical address and the second is the logical address.
The physical address is known as MAC address and the logical address is known as IP address.
Physical address i.e. MAC address identifies a device in the local network and IP address identifies the device globally.
A network packet requires both addresses to reach its destination i.e. from sender to receiver.
In today's article, we are going to talk about MAC address.
What is the MAC address?
MAC address is a physical address used to uniquely identify each device on the network. The full form of the MAC address is the Media Access Control Address.
The MAC address is present in every network interface card (NIC) and cannot be changed.
Since there are millions of devices on the network, and each device must have a unique MAC address, MAC addresses are made up of six two-digit hexadecimal numbers, separated by colons.
There is no need to remember these, as they are automatically recognized by most networks.
MAC address works at the data link layer of the OSI model. This is a 48 or 64-bit address associated with the network adapter.
MAC addresses are tied to the hardware of the network adapter, so they are also known as “Hardware Addresses” or “Physical Addresses”. It specifically identifies the adapter on a local area network.
MAC addresses are expressed in hexadecimal notation. For example, “01-23-45-67-89-AB” in a 48-bit address or “01-23-45-67-89-AB-CD-EF” in a 64-bit address.
Sometimes, a colon (:) is used instead of a dash (-). MAC addresses are often considered permanent, but in some situations, they can be changed.
Summary
- MAC address is also known as physical address, hardware address, and burnt-in address.
- MAC addresses are typically assigned by the manufacturer of the network interface card (NIC).
- MAC addresses are expressed in hexadecimal notation. This is a 48 or 64-bit address
- The first 24 bits are used for the Organization Unique Identifier, and the next 24 bits are for the NIC manufacturer.
- MAC addresses are permanent and cannot be changed.
- Two devices cannot have the same MAC address. If this happens, both devices will have communication problems because the local network will become confused as to which device should receive the packet.
- The MAC address is created using specifications provided by the IEEE.
- It works at the Data Link Layer of the OSI model.
- It is provided by the device manufacturer at the time of manufacturing and is embedded in its NIC.
- The ARP protocol is used to associate a logical address with a MAC address.
Types of MAC Address
There are three types of MAC addresses :
- Unicast mac address
- Multicast mac address
- Broadcast mac address
1) Unicast MAC address
The unicast MAC address represents a specific NIC on the network. The MAC address of the source machine is always unicast.
2) Multicast MAC Address
Multicast addresses enable the source device to transmit data frames to multiple devices or NICs. In a Layer-2 (Ethernet) multicast address, the first 3 bytes of the first octet of the LSB (least significant bit) are set to one and reserved for the multicast address. The remaining 24 bits are used by the device that wants to send data in a group.
3) Broadcast MAC Address
It represents all the devices within a network. In broadcast MAC address, the Ethernet frame containing all the bits of the destination address (FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF) is known as the broadcast address.
If a source device wants to send data to all devices within the network, it can use the broadcast address as the destination MAC address.
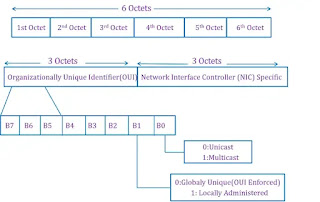
Format of MAC Address
The MAC address is a 12-digit hexadecimal number (6-byte binary number), mostly represented by colon-hexadecimal notation. The first 6 digits of the MAC address (e.g. 00:40:96) identify the manufacturer, called the OUI (Organizational Unique Identifier). The IEEE Registration Authorization Committee assigns these MAC prefixes to its registered vendors.
Here are some OUIs of famous manufacturers :
- CC:46:D6 – Cisco
- “00-14-22” – Dell
- 3c:5a:b4 – Google, Inc.
- 3C:D9:2B – Hewlett Packard
- 00:9A:CD – Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd
The rightmost six digits represent the network interface controller, which is assigned by the manufacturer.
Why is the MAC address used?
A MAC address is a unique number used to track a device on a network. MAC addresses provide a secure way to locate senders or receivers in a network and help prevent unwanted network access. MAC address is also used to identify a specific device in the Wi-Fi network at the airport.
How to find out the MAC address?
We can easily find or check the MAC address of any computer device. For this, you will have to open the command prompt of your computer, which you can do by following the steps given below.
MAC address on Windows
- Click Windows Start or press the Windows key.
- Type cmd in the given search box to open Command Prompt.
- Press the Enter key, and then you will see the command prompt window, after this, you have to type the command given below in it.
- ipconfig/all
- After typing the above command now press the enter key.
- It will display different information, scroll down, and look for the physical address. This physical address is the MAC address of your device.
As we can see in the above image, two physical addresses are shown with different values, one is for the Ethernet adapter, and the other is for the VMware network adapter.
Finding MAC Address on Macintosh OS
Follow the steps below to find the MAC address on the Macintosh OS :
- Open the Apple menu, and click System Preferences.
- System Preferences. Under → Select Network →
- The above path will open a network box.
- Select the Wi-Fi option from here. It will show a Wi-Fi address or airport address display; This is the MAC address of your device.
Difference between MAC address and IP address
- MAC address means Media Access Control Address. Whereas IP address means Internet Protocol address.
- MAC address is a 48-bit address whereas an IP address has a 32-bit address.
- MAC address works at the data link layer of the OSI model while IP address works at the network layer of the OSI model.
- A MAC address is called a physical address while an IP address is called a logical address.
- Classes are not used in MAC addresses whereas in IP, IPv4 uses A, B, C, D, and E Classes.
- MAC address is a unique address provided by the manufacturer whereas IP address is provided by the ISP.
Learn More...
- What is Java? Why and how to learn Java Language?
- What is Web Page?
- What is C++? History & Features of C++ Language
- What is Intranet?
- What is the difference between Prepaid and Postpaid? | Which Sims Card is good for you?
- What is ROM? | How many types of ROM are there? | Full Form of ROM
- What is Encryption?
- What is High Level Language? | Types | Advantages & Disadvantages of high level language
- What Is Plotter?
- What is Virtual Reality?
- Features of java language
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Internet
- How To Format Hard Disk Windows 10,11 | How to format hard disk through command prompt in Windows computer?
- What is WordPress? Types of WordPress and its benefits
- What is Google Authenticator? Know about this tool for online security..!!
Conclusion
in today's article, we talked about MAC address and learned what is MAC address? How does MAC address work?
I hope you liked this article and if you liked this article then do not forget to share this article with your friends so that they can also get information about what is MAC address.
If you still have any questions or doubts related to the MAC address in Hindi, then you can ask us through comments. I will answer all your questions and for more information, you can contact us.
To get similar information related to technology, computer science, and networking, subscribe to our website. So that you will get information about our upcoming new posts quickly.